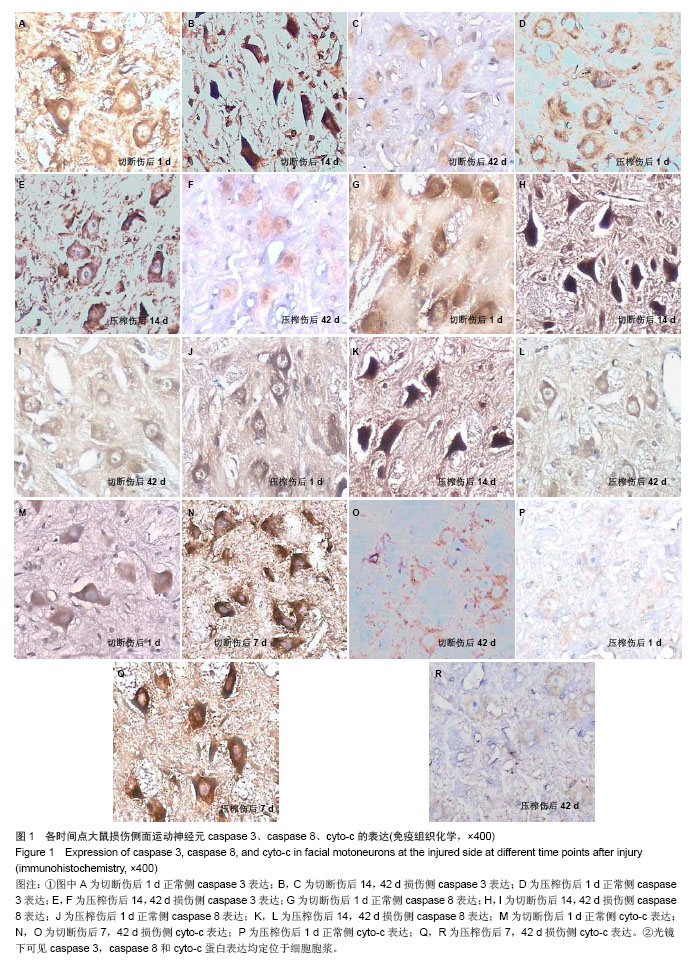
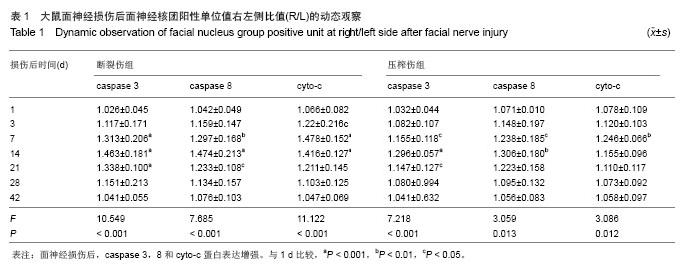
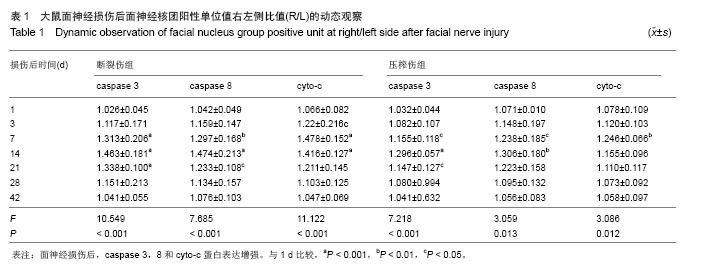
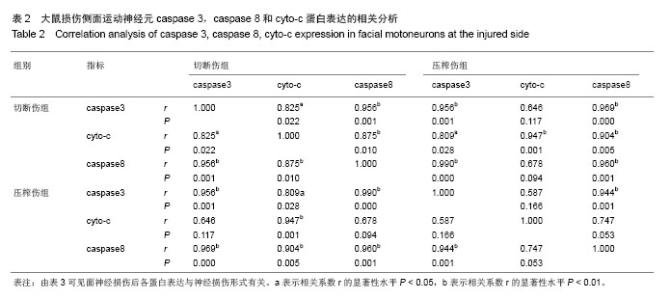
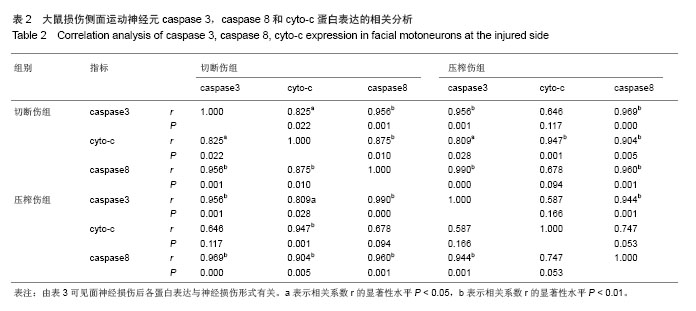
| [1]李蜀光,魏海刚,许彪,等.面神经损伤后面运动神经元死亡的时间进程及电镜观察[J]. 广东医学,2007,28(8):1240-1242.
[2]De Bilbao F, Dubois-Dauphin M. Time course of axotomy- induced apoptotic cell death in facial motoneurons of neonatal wild type and bcl-2 transgenic mice. Neuroscience.1996;71(4): 1111-1119.
[3]Gorman AM, Orrenius S, Ceccateli S. Apoptosis in neuronal cells: role of caspases. Neuro Report.1998, 9: R49-R55.
[4]魏海刚,许彪,吴荣忠.半胱氨酸天冬酰胺蛋白酶与面神经损伤[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志,2002,12(1):47-50.
[5]Gabriele U,Cedric R,Anna F,et al.Fas/Tumor necrosis factor receptor death signalingIs required for axotomy-induced death of motoneurons in vivo. Neuroscience. 2003;23(24): 8526-8531.
[6]Park OH, Lee KJ, Rhyu IJ, et al.Bax-dependent and-independent death of motoneurons after facial nerve injury in adult mice.Eur J Neurosci.2007;26:1421-1432.
[7]Guarin E, Seuret P, Nef S, et al. cpp32 messenger RNA neosynthesis is induced by fatal axotomy and is not regulated by athanatal Bcl-2 over-expression. Neuroscience.1999;90: 653-664.
[8]Fujimura M, Morita-Fujimura Y, Murakami K, et al. Cytosolic redistribution of cytochrome c after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.1998;18(11): 1239-1247.
[9]Chen J, Nagayama T, Jin K, et al. Induction of caspase-3-like protease may mediate delayed neuronal death in the hippocampus after transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 1998;18(13): 4914-4928.
[10]Casha S,Yu WR,Fehling MG, et al.Oligodendroglial apoptosis occurs along degenerating axons and is associated with Fas and p75 expression following spinal cord injury in the rat. Neuroscience.2001;130(1): 203-218.
[11]Endres M, Namura S, Shimizu-Sasamata M, et al. Attenuation of delayed neuronal death after mid focal ischemia in mice by inhibition of the caspase family. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998;18(3): 238-247.
[12]kutan O,Solaroglu I,Beskonakli E,et al.Recombinant human erythropoietin decreases mye|operoxidase and caspase-3 activity and improves early functional results after spinal cord injury in rats.J Clin Neurosci.2007;14(4):364-368.
[13]苏建华,章莉萍,陈玉芳,等.丁咯地尔对大鼠坐骨神经损伤后背根神经元凋亡及Caspase-3、Bcl-2表达的影响[J].广西医科大学学报,2010,27(6):855-857.
[14]葛洪亮,贺茂林,李世德.蛇毒神经生长因子对大鼠脊髓损伤后Caspase-3表达影响[J].蛇志,2011,23(2):111-113.
[15]沙鲁佳妮.脱细胞神经支架修复坐骨神经损伤后脊髓神经运动元内FasL和Caspase-3的表达[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2011.
[16]于洋,黄绍辉,王绪凯.面神经损伤诱导面神经元死亡及其调控基因表达的实验研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2009,2(11): 670-672.
[17]于洋,黄绍辉,刘敏达,等.面神经损伤后MnTBAP对面神经元的保护作用[J].中国医科大学学报,2010,39(11): 915-918.
[18]洪华兴,洪正华,陈海啸,等.促红细胞生成素抑制大鼠脊髓损伤后caspase -12表达的研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(2):183-185.
[19]袁婧.NGF不同给药方式对面神经损伤后运动神经元凋亡及PUMA,caspase-3表达的影响[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2013. |